
7).īipolar disorders are not as obviously influenced by hereditary and biological factors as neurodevelopmental and schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Rather, the evidence supports attributing these severe disorders to an underlying biological problem (Centers for Disease Control, 2011, p. Although it has been proposed in the past (c.f., Kanner, 1943), there is no evidence to suggest that faulty parenting is the cause of autism or schizophrenia. Individuals with these diagnoses appear to differ from “normal” individuals qualitatively rather than quantitatively. Autistic (including many fragile X) children and schizophrenic adults are usually physically indistinguishable from their peers however their defining symptoms are extreme and easily identifiable. For example, Down syndrome children have distinct anatomical features making them easy to identify. Neurodevelopmental disorders appear too early in life for nurture to have a major influence and the symptoms can be physical as well as behavioral. The importance of nature (heredity and biology) in neurodevelopmental and schizophrenia spectrum disorders is readily apparent. doi:10.Chapter 11: Problems in the Development of Human PotentialĭSM 5 – Bipolar, Depressive and Anxiety Disorders Bipolar and Related Disorders The Role of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) in Bipolar Disorder: Effectiveness in 522 Patients with Bipolar Depression, Mixed-state, Mania and Catatonic Features. Perugi G, Medda P, Toni C, Mariani MG, Socci C, Mauri M. Managing the side effects associated with commonly used treatments for bipolar depression. Identification of pathways for bipolar disorder: a meta-analysis. Nurnberger JI Jr, Koller DL, Jung J, et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Cyclothymia: The "Primacy" of Temperament. The National Center for Biotechnology Information. Impact of the DSM-IV to DSM-5 Changes on the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Rockville (MD): Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US) Table 12, DSM-IV to DSM-5 Bipolar I Disorder Comparison. DSM-5 Changes: Implications for Child Serious Emotional Disturbance. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Prevalence and description of psychotic features in bipolar mania. Catatonia: Our current understanding of its diagnosis, treatment and pathophysiology. Rockville (MD): Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US) Table 3.8, DSM-IV to DSM-5 Hypomania Criteria Comparison. Rockville (MD): Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (US) Table 11, DSM-IV to DSM-5 Manic Episode Criteria Comparison.Īmerican Psychiatric Association.

For example, someone may experience the extreme agitation and restlessness associated with mania and the suicidal thinking more attributed to depression at the same time during a mixed episode Mixed episodes (or mixed affective states) are periods where mania and depression occur at the same time.Typical symptoms include a mix of intense and severe feelings of despair, hopelessness, sadness, and worthlessness or guilt appetite changes, sleep disturbances, agitated behaviors, including pacing or hand wringing frequent thoughts of death or suicide and difficulties in making decisions and concentrating Major depressive episodes are periods of emotional and energy lows that persist for at least two weeks.Unlike mania, these episodes are not severe enough to lead to hospitalization or significantly impair social or occupational functioning Hypo means "under," and it is used in hypomania because this mood state is under, or less manic, than mania. Hypomanic episodes are also defined by distinct periods of abnormally and persistently elevated or irritable moods, but hypomanic episodes last for at least four consecutive days and present at most hours of the day nearly every day.
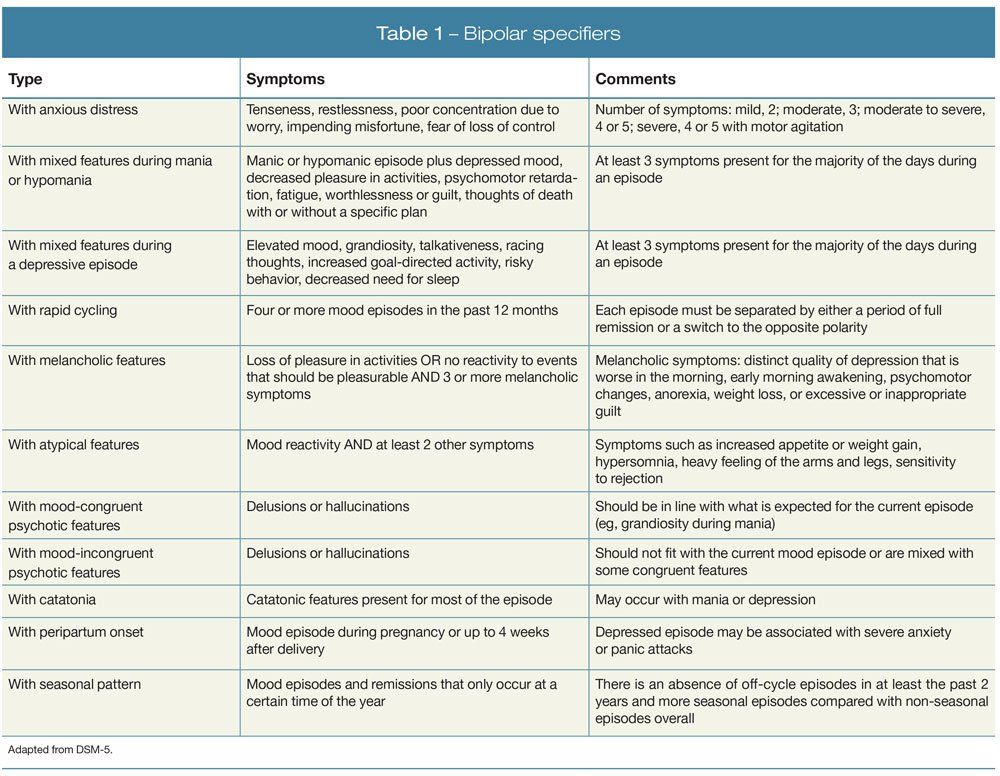
Manic episodes can cause marked social or occupational impairments when they are severe. The average age for people with bipolar disorder to experience their first manic episode is 18, but a first manic episode can happen anytime from early childhood to late adulthood


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
